每日一题-2
# 1506G Maximize the Remaining String
Codeforces Round #710 (Div. 3) (opens new window)
题意,找出字符串s的一个子序列s‘,满足s'的字符集等于s的字符集(即每个在s中出现的字符都在s‘中出现),且s'中的每一个字符都是unique,且s'的字典序最大。
QAQ思路不够活跃,想不出来解法,但是我的代码比标答快一个数量级……
从t=空字符串 开始构建s’
每次往t后面push一个字符c,c需要满足:我怎么想不到这样构造,一直在想怎么从大到小或者从小到大遍历字符集
- t是s[1...i] 的子序列,且i最小
- s[j]=c,
且j最小(贪心) - s[j...n] 包含字符集里除了 t之外的所有字符
我们每次选择满足上述条件的最大c,这样最终的s'就是字典序最大的
我的做法时间复杂度是
点击展开
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int t;
vector<int> q[26];
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
string s, t;
int n = 0;
set<int> cr;
cin >> s;
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
q[s[i] - 'a'].push_back(i);
for (int i = 0; i <= 25; ++i)
{
if (q[i].empty())
continue;
sort(q[i].begin(), q[i].end());
n++;
cr.insert(*q[i].rbegin());// 每个字符出现的最后位置
}
int curi = -1;// t是s[1...curi] 的子序列,且curi最小
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
for (int j = 25; j >= 0; --j)
{
if (q[j].empty())
continue;
//j=q[i][curj],s[j]=c,j>i且j最小
int curj = lower_bound(q[j].begin(), q[j].end(), curi) - q[j].begin();
//s[j...n] 包含字符集里除了 t之外的所有字符
if (cr.empty() || *cr.begin() >= q[j][curj])
{
t.push_back('a' + j);
curi = q[j][curj];
cr.erase(*q[j].rbegin());
q[j].clear();
break;
}
}
}
cout << t << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
# 1506F. Triangular Paths
Codeforces Round #710 (Div. 3) (opens new window)
题意比较长……
不好用语言描述,多画几行,不难发现
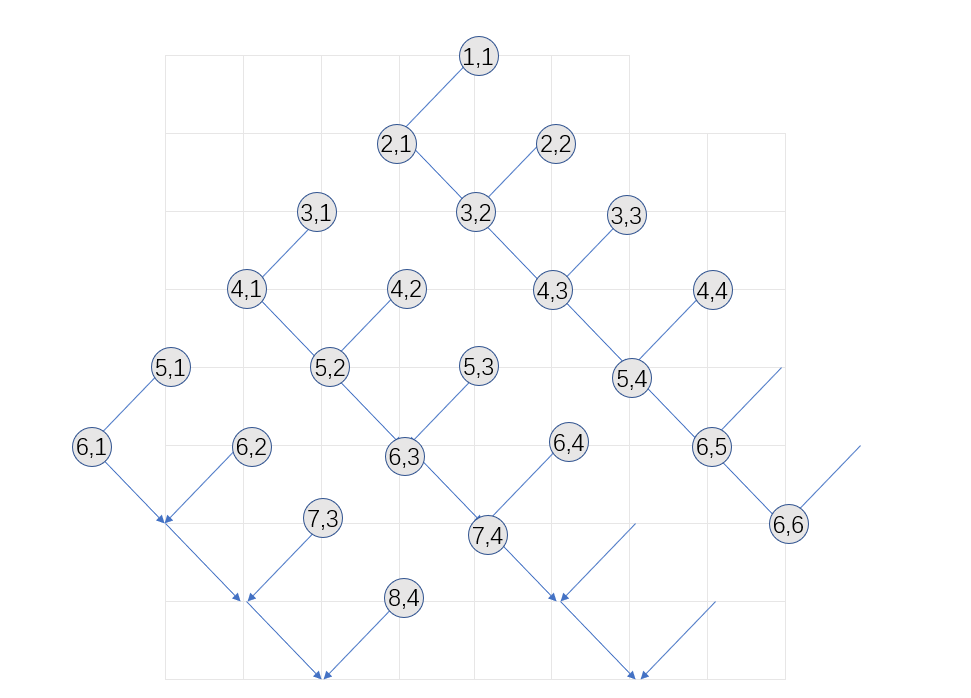
不难发现图形是很规律的锯齿形,我们可以根据
如果
,即从连线到锯齿,不能到达。比如2,1到2,2或者3,3 ,不能直接到达,此时必须不断修改锯齿的朝向,比如1,1到3,3只能1,1到2,2到3,3(由1可知,到2,1不能到3,3),花费是 其他情况都快直接到达,花费0
如果
点击展开
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#ifdef DEBUG
const int ms = 100 + 5;
#else
const int ms = 2e5 + 5;
#endif
typedef long long ll;
pair<int, int> a[ms];
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
int n;
cin >> n;
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i].first;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i].second;
a[i].second = a[i].first - a[i].second;
}
sort(a, a + n);
int res = 0, c1 = 0, e1 = 0, r = 1;
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int c2 = a[i].second / 2, e2 = a[i].second % 2;
if (c1 != c2)
{
e1 = 0;
res += c2 - c1;
}
else if (e1 == 0 && e2 == 0 && c1 == c2)
{
res += a[i].first - r;
}
c1 = c2, e1 = e2, r = a[i].first;
}
cout << res << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
# 1495B Let's Go Hiking
Codeforces Round #706 (Div. 1) (opens new window)
A和B做游戏,有一个排列P,长度为n,AB一开始各选择一个位置x,y,A先手,A只能往比他当前小的地方走,B只能往比他当前小的地方走,A和B的位置不能重复,问有哪些位置A先手必赢。
首先排除首尾,B站A旁边就卡死了。
因为P是排列,所以P可以抽象成
我们可以排除除了峰顶的所有位置,考虑A站在
站在峰顶上,如果峰顶两侧的长度不同,B只需要站在长坡上,距离峰顶位置大于短坡长度的奇数位置,A必输,比如1,2,4,3,A站在P[3]=4,B只需要站在P[2]=2即可,由于峰顶两侧的长度不同,必存在这样的奇数位置。
如果峰顶两侧的长度相同且都为奇数,B只需要站坡底,A必输 比如1,2,3,7,6,5,4
如果峰顶两侧的长度相同且都为偶数,B和A站在同一个坡上必输,这时候需要考虑其他坡有没有长度大于等于当前坡的。
点击展开
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#ifdef DEBUG
const int ms = 100 + 5;
#else
const int ms = 2e5 + 5;
#endif
int a[ms];
// 以i为起点,往左下降的长度,右下降的长度,i左边最长的坡长度,右边的坡长度
int dl[ms], dr[ms], mdl[ms], mdr[ms];
bool check(int i)
{
if (dl[i] == 0 || dr[i] == 0)
return false; // 单边为0不行
int m = max(dl[i], dr[i]);
if (dl[i] != dr[i])
return false; // 不等必输
// 偶数且坡最长
return (m % 2 == 0) && max(mdl[i - dl[i]], mdr[i + dr[i]]) < m;
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(nullptr);
int n;
cin >> n;
if (n <= 2)
{
cout << "0\n";
return 0;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
if (i > 0)
{
if (a[i] > a[i - 1])
{
dl[i] = dl[i - 1] + 1;
}
mdl[i] = max(dl[i], mdl[i - 1]);
mdr[i - dl[i]] = max(mdr[i - dl[i]], dl[i]);
}
}
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (a[i] > a[i + 1])
{
dr[i] = dr[i + 1] + 1;
}
// 1 2 3 7 6 5 4 对于1上升和下降都要考虑到。l同理
mdr[i] = max(mdr[i], max(dr[i], mdr[i + 1]));
mdl[i + dr[i]] = max(mdl[i + dr[i]], dr[i]);
}
int res = 0;
for (size_t i = 1; i < n - 1; i++)
{
if (check(i))
{
res++;
}
}
cout << res << "\n";
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69